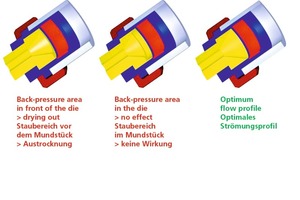
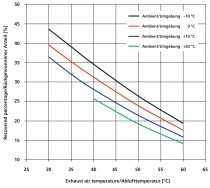
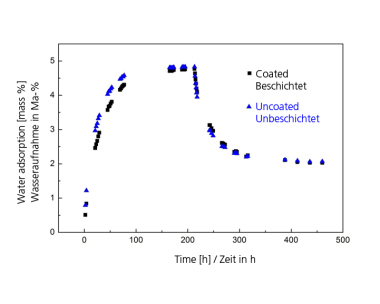
Energy saving processes for brick shaping
Research project conducted by the Research Alliance of the Clay Brick and Tile Industry Regd (FGZ)
Project number
AiF 17273 N
Project funded by
BMWi through the German Federation of Industrial Research Associations “Otto von Guericke” Regd (AiF)
Realized by
Brick and Tile Research Institute Essen Regd. (IZF)
Project manager
Dipl.-Ing. (FH) M.Sc. Alexander Winkel and Dipl.-Ing. Eckhard Rimpel