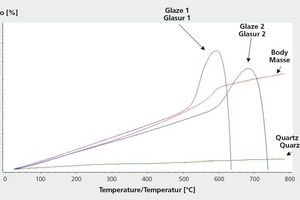
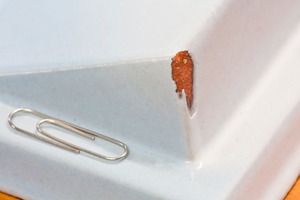
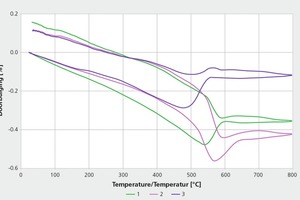
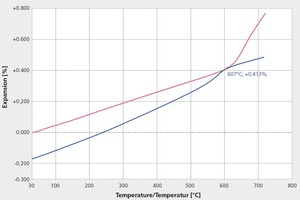
Controlling glazes – Avoiding hair cracks and chips
Glaze and body must always bond to one another to prevent creation of hair cracks in the glaze, or to prevent pieces of glaze from chipping off the underlying body. The article shows which aspects play a role in this bonding process and which laboratory measuring methods prior to production lead to the best insight about possible risks.
1 Introduction
A glaze is a thin glassy layer bonded to ceramic in the firing process, with the objective to obtain certain aesthetic properties, improve the sustainability of the object it is applied to, obtain a smooth surface and/or make it waterproof. Glazes can be transparent or opaque, matt or glossy, and there are many colours.
A glaze usually consists of a network of interconnected silicon tetrahedra that ensure coherence and binding. Oxides of boron and aluminium also contribute to this network structure. They are referred to as network creators. In contrast, many oxides such as those...