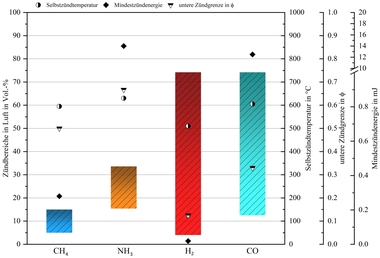
During firing of brick products, factors such as expansion and shrinkage processes, endothermic and exothermic reactions as well as mineral phase transformations play a significant role. In the course of the firing process, stress tolerance limits are often exceeded, so that the danger of quality-impairing damage such as cracks, spalling, deformation and microstructural damage increases. Besides the visible damage, especially cracks inside bricks, for example web cracks in lattice bricks or microstructural damage in solid bricks, are difficult to detect. They are, however, a severe quality...