Efficiency measures in industry – possibilities with cogeneration of heat and power
Optimum utilization of energy is becoming increasingly important for industrial enterprises in Germany. One component for this is the introduction of cogeneration for heat and power (CHP).
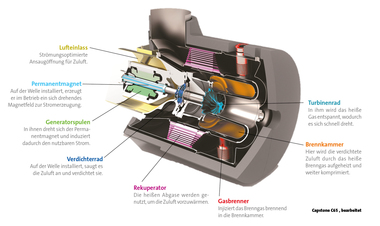
During the combustion of natural gas in gas engines or turbines, in addition to power, heat is generated in different forms. To obtain a technically and economically optimized solution tailored to the needs of an industrial enterprise, careful determination of the time availability and output of the required energy form, such as power, steam, heat or cooling, is a precondition. In many applications, the utilization of the released heat is the limiting factor for the dimensioning of the CHP plant.
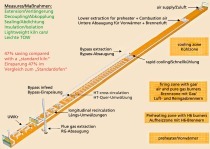
In the ceramics and heavy clay industries, the heat generated can be used for drying, steam generation, but also for incorporation, for example, in suitable zones of kilns.
Despite the change in the legislative framework, in accordance with the German Renewable Energy Act (EEG) dated 2014, also in the case of in-plant energy generation, 40 % of the EEG levy must be paid. Even if, according to the draft bill for Germany’s new Heat and Power Cogeneration Act 2015, the “CHP” bonus (support for operating time of 30 000 operating hours) will be phased out for many industrial enterprises, CHP plants remain technically and economically expedient measures to complement energy supply to industrial operations providing the plants are selected and operated properly.
Peter König, AGO AG Energie + Anlagen